A guide to automotive electrical repair
The car’s electrical system is a fundamental part of a vehicle’s operation. By utilizing an intricate wiring system, it powers an array of parts like the windshield wipers, car windows and many more. Each system has its own differences depending on the car’s model, make an age. Some newer car models have integrated a complex computer system that interacts with some car functions like the brakes, steering various sensors and more.
What are the electrical components of a car?
Parts of an automotive electrical system
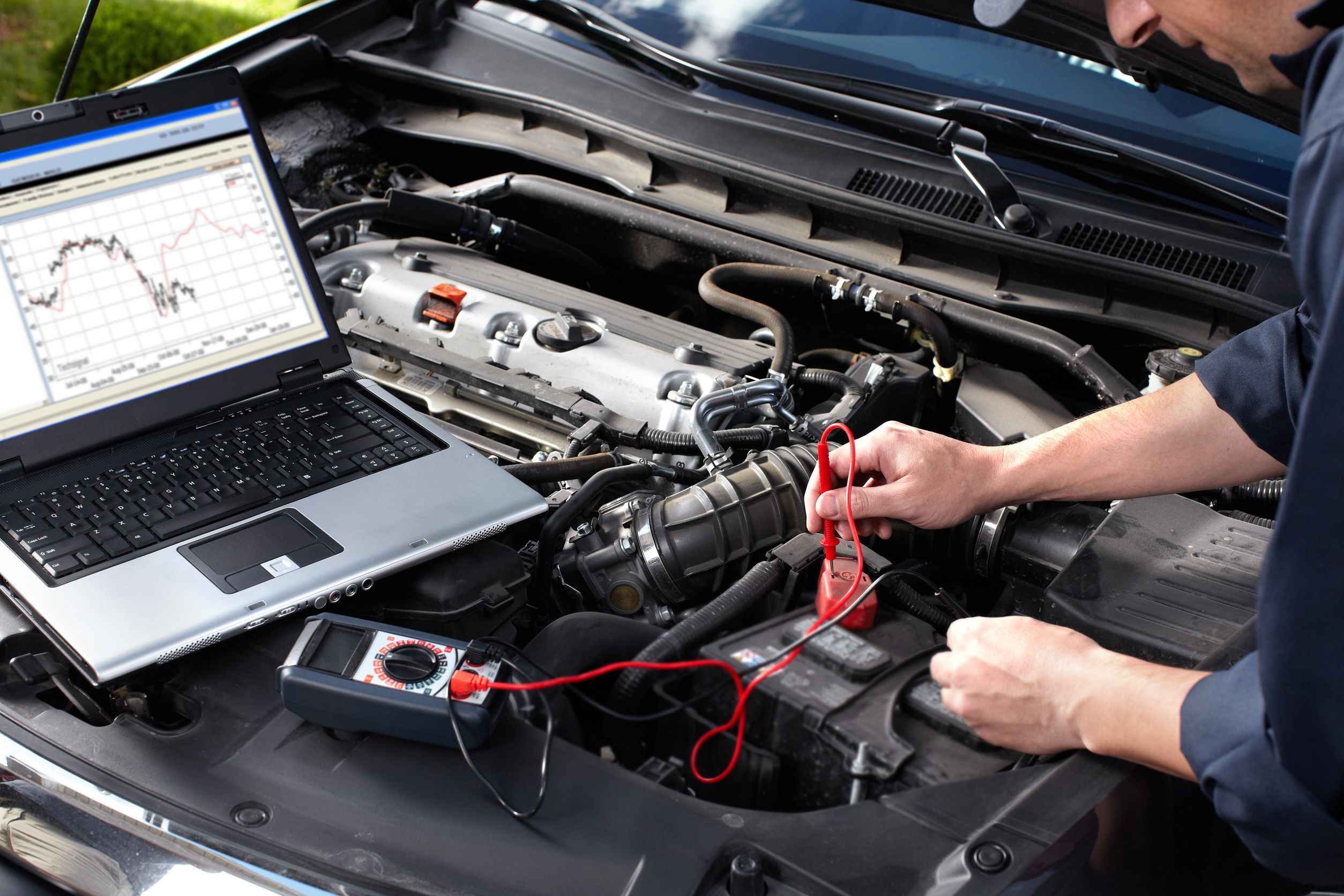

Photo on autoelectriclisnaskea.com
A cars’ electrical system is a closed circuit powered by the battery. They are responsible for routing power, information, ground signals, and serial data communication between the vehicle’s controls the systems. It Includes the starter, battery, and the alternator. Apart from the main charging, ignition and starting circuits, there are others that power the lighting, electric motors, sensors, and gauges of electrical instruments, heating elements, the AC, magnetically operated locks, the radio and more. All these systems are linked by wiring, fuses, circuit breakers, and electromagnetic relays. Loose or broken wiring, bad connectors or switches can result in loss of power an and inoperative system. All this work is done by these major components that make up the vehicular electrical system:
- Battery – It supplies power to the car and also powers some components when the engine is not running.
- Ignition coil or the fuel pump switch – Petrol/ Gas engines need a spark to fire up the cylinder. For diesel engines, the pump has to be constantly on, to keep injecting fuel into the engine so it can run. This is done by a solenoid switch. It is hard to know when a starter will fail but checking the electrical system can help you see the warning signs.
- Alternator/ Dynamo or the power generator – It is made up of various parts that are contained in an aluminum housing. It generates electricity by drawing power from the engine. It Makes enough electricity to power many of the electrical components. Your car can start with a defective alternator but it will not run for long. A faulty alternator can cause the electrical system to be volatile, discharge the battery an cause engine failure.
- Cooling fans – in earlier car models, radiator cooling fans were paired together with the engine. But with the technological advancements made it is now controlled electronically, turning on only when needed.
- Air conditioner blower – this is another fan that allows for air circulation from the air conditioner to the car’s cabin.
- Wiring – This is a vast, intricate network of wires that connect the many components of the electric circuit to the battery. The large battery cables transmit several amps of current while the smallest wires can transfer only milliamps to sensitive sensors and computer systems in the car.
- Starter motor – it is responsible for cranking the car to start the engine and is powered by the battery.
- Lighting – this includes the head and tail lamps, blinkers, brake lights, and more. These are wired to a central circuit running throughout the whole car.
- Motors/ Actuators – these include wipers, power windows, power steering, and others. They perform various functions in the car.
- The Electronic Control Unit – it is the onboard computer that manages many of the functions of the car
- Fuse boxes and relays – they moderate the current in the car. Fuses prevent the frying of these components in the event that the alternator, wiring or the battery are faulty. Relays handle the switching of heavy electrical components in the car.
- Combination Switch – this is the switch assembly that is usually found under the steering wheel an is used to control the headlight, brake lights, wipers an so on.
- Peripheral systems – these control the stereo, clocks, cabin and trunk lights.
- Signal transmission – these include a range of sensors and transmitters for tire pressure, fuel and oil levels, crash sensing, cameras and more.
How does the electrical system in a car work

Photo on dhallaautomotive.com.au
The system works to deliver and monitor electrical power to various devices and sensors under the control of a computer system or a person in the car. Here is a quick overview of how gas engine-powered vehicles use electricity and various electrical system components.It provides the electrical current needed to run the ignition and fuel systems, which are responsible for creating the combustion needed for the proper function of the engine. The starter gets the engine working. The battery provides some power to the starter motor, which rotates the flywheel that turns the crankshaft which moves the engine’s pistons. While the engine is running, the alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy thereby keeping the battery charged. They are driven by a belt and use a small signal from the battery to energize a field current the turns a rotor. Because the energy is driven by the polarity of magnetic fields, it changes the rotation of the rotor resulting in the production of AC current. Alternators produce higher currents than the battery, and that is used to recharge and power some of the electrical components. Most of the components, however, need DC current to operate. This is solved by the use of diodes that convert AC to DC power.
Not all components use the same amount of amperage. Fuses and volt regulators help moderate the flow of electric current while protecting the components.While the voltage of a car’s electrical system is much lower than that of a house, it is still vital to enlist a professional when making a diagnosis or before starting repairs, because most of the components are highly sensitive.
What causes electrical problems in a car?
Diagnosing car electrical problems
Photo on consumerreports.org
The cause for electrical failure in a car can vary. This involves checking the battery, the adjoining cables, and the sensitive electronics to see if they are working well. The most common culprit, however, is the battery. With newer car models and technological advancements, this introduces more ways for something to go wrong. Here are some of the problems that may occur:
Bad or dead battery – It is the source of electricity in the car, so if there is a complete electrical failure, the battery is to blame. If the car won’t start the battery is most likely dead. Here are a few reasons why a car battery would fail:
- Leaving the headlights or dome lights on overnight. It’s normal for headlights to remain on for some time but a function can leave them on overnight, that will drain the battery.
- The battery is weak or in poor condition, this means it has low capacity. This can be due to poor maintenance or old age.
- Corroded or loose battery connections will cause the battery not to charge properly.
- Parasitic drains to the electrical system. These can be difficult to find like the glove box or trunk lights that turn on when they shouldn’t or they remain on when they should be off.
- Extreme temperatures can cause battery failure especially if the battery is weak or old by magnifying underlying issues.
- A faulty charging system. The cause of this may be a failing alternator or faulty wiring.
A defective alternator – The alternator is usually fixed to a belt system that spins due to the engine turning, creating power that powers the car and charges the battery. A faulty alternator can cause the battery to be drained quickly. Here are some reasons why the alternator would fail:
- It is dead – the typical lifespan of an alternator is 5 – 7 years. If this time has lapsed and you are having electrical issues then maybe the alternator is worn out and need to be replaced.
- A computer problem- newer car models come with an inbuilt computer system that virtually manages most of the car’s components, the alternator included. Any malfunction in the system could cause the alternator to stop working. In the case of this kind of failure, there will be more signs to indicate computer failure.
- Faulty wiring with the many wires that deliver power to the alternator one may become faulty or worn out causing the alternator to fail.
- Bad or blown fuses – some vehicles use fuses to keep the alternator functional. If they happen to blow out due to wear or a power surge, the alternator will fail and not charge the battery.
- Broken pulley or broken belt – alternators use the mechanical power of a belt and pulley to create electricity from the engine. This means that they will undergo a fair amount of wear and tear. The pulleys last longer and have to get significantly damaged before they need to be replaced, belts are more fragile and will often break. If either of this happens, the alternator will not function well. The alternator can produce growling or whining sounds that are a result of a loose or damaged fan belt or pulley, or a worn out alternator bearings.
- A faulty alternator can cause overcharging of the battery.
- The warning light will often light up when the electrical components in your car do not perform as they should.
The headlights or dash lights are dim or flicker – This is a common symptom of alternator failure. Dim and flickering lights go hand in hand. To be sure that it is an alternator problem look at how the lights behave when you use something like the radio that uses a lot more electricity.
There is a clicking sound when trying to start the engine
- A rapid like firing sound indicates a lack of electrical power either due to low voltage or high resistance. Low voltage may be due to a weak or low battery. The high resistance may be due to a loose battery cable end, corrosion of the cables and battery posts, loose connections or a faulty cable to starter or ground connection.
- If you hear a single click, then the contacts in the stater’s solenoid are worn out or corroded and they develop such high resistance that when you try starting the car, they use up the voltage meant for the starter.
There is a burning plastic smell – This is an indicator of an electrical short circuit. The smell comes from the burning of the plastic that covers the wires, connections or fuses. A burning rubber smell can also come about if the drive belt melts, this will, in turn, cause the alternator to fail.
The fuses are blown – If there is sudden power loss in one area such as the headlights, radio or brake lights, check the fuse box. The whole vehicular electric system is connected via the fuse box so as to regulate the amount of power going to each system. If a particular system fails simply replacing the blown fuse should solve it.
You have had to jumpstart your car recently this simply means your battery was drained.
Faulty wiring – Wires connect all the electrical components to the power sources. A faulty wire means a broken circuit and this will result in failure of the connected component.
Misfiring or bad spark plugs – These are tiny but essential parts of a car. They ignite the compressed fuel in an internal combustion engine. Misfiring spark plugs can affect the engine’s power an fuel efficiency and cause damage to the catalytic converter. Signs of bad or misfiring spark plugs include poor acceleration, rough idling, and the vehicle engine cranking but not starting.
When should you have the car’s electrical systems checked? When you notice any of the previously mentioned red flags or warning signs, it is important to get the car checked.
How do you fix electrical problems in your car?
Troubleshooting car electrical system issues

Photo on 123carandcommercial.com
Trying to pinpoint the exact problem when it comes to electrical issues can range anywhere from a dead battery to a faulty wire in the car’s wiring. There are some ways to troubleshoot electrical problems in a car:
- Open the hood and inspect the battery. Look for signs of corrosion or loose cabling. If there are signs of corrosion present clean it off with a cleaning solution and a wire brush.
- Also check on the alternator; the belt, and wiring. Look for signs of cracking or if the belt has become loose or is fraying. This will warrant immediate replacement of the belt as a bad belt can make even a good alternator run poorly. Ensure that the wiring to the alternator is working well.
- Look at the spark plugs and wires. Ensure that the wires are properly secured on both ends and the spark plugs are tightened securely and are not corroded.
- Make sure to test all the wiring to ensure that they are conducting electricity as needed.
- When you experience electrical problems like dimming lights, the radio not turning on among others then this is an indicator your electrical system is faulty.
How do you maintain your vehicle’s electrical system?
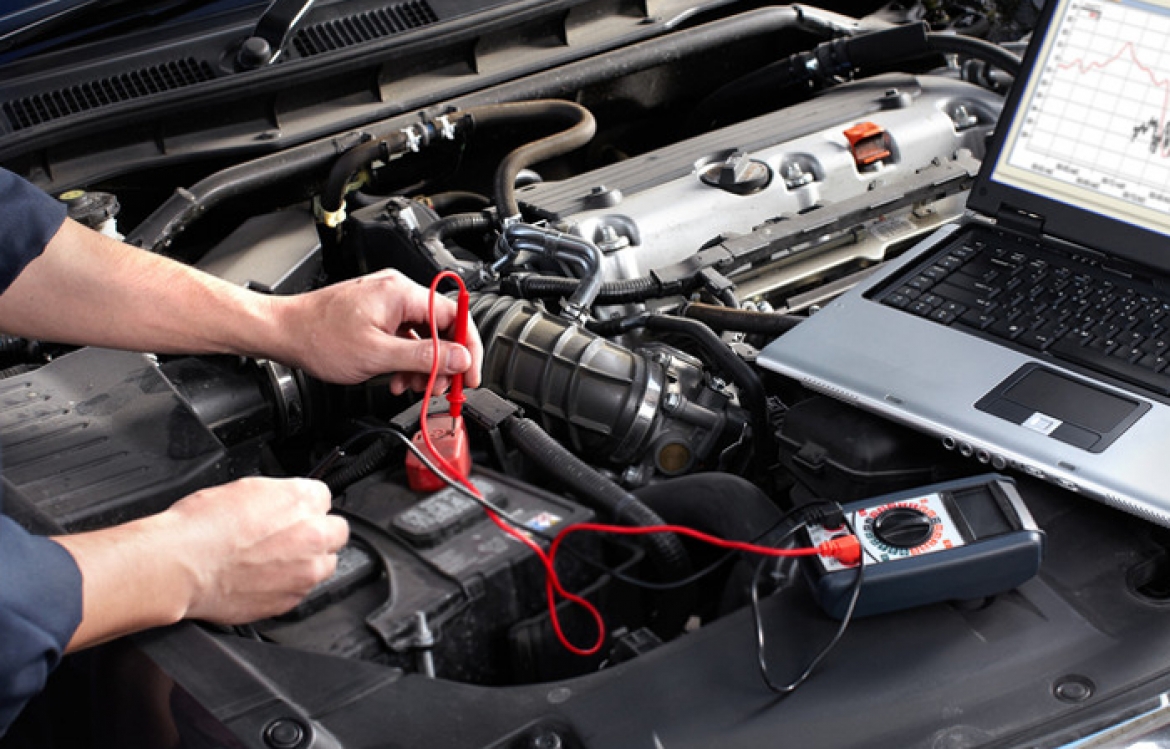

Photo on autoelectricrepair.net
The car’s electrical system undergoes a lot of wear and tear and needs constant maintenance to avoid failures and problems. The following are some ways you can properly care for the battery, starter, and alternator:
a. Check and regularly clean the battery and its cablesThe posts and battery cables can be corroded. It is recommended to check the battery and cables monthly to ensure there is no build up of corrosion. If there is some corrosion, clean the area with a solution of baking soda and or a corrosion removal fluid. Here is how you clean the battery posts and cables of corrosion:
- Remove the battery cable from the posts
- Using a wire brush and the cleaning fluid clean the posts
- Rinse the battery cables and posts with clean water
- Reconnect the battery cables starting with the positive side first.
b. Check on the drive belt monthlyLook for cracks, dryness and/or grazing along its surface. It is also vital to check on the tension of the belt. This will help you know if you need to replace the beltc. If the battery of your car is more than 5 years oldThe older your car battery gets, it loses its capacity to hold a charge and you may not be able to start the car. In this instance, you will have to replace the battery. With proper maintenance and recharging the battery can last longer. Parking the car for a very long time can cause faster deterioration of the battery. Cold weather can also cause the car not to start when the battery is low on charge.d. Replace all parts that cannot be fixed
The cost of repairing some of these parts is highly dependent on the car’s make, model and age.
