Is recharging really not recharging?
Nanoflowcell is a Swiss company that has been discussing a new concept in electric cars for years. It will be displaying its latest model, the Quant 48VOLT, at the Geneva Motor Show next month. It is an electric car, but it cannot be recharged the traditional way. This makes it unique. Instead, the battery is recharged like a regular gas tank for a gasoline engine. Here’s the scoop on flow batteries.
NASA in 1976 patented the idea. NASA invented the idea to find a better way of storing energy for space travel. It can take batteries a while to charge and then to release stored energy. This is not an issue with supercapacitors. Flow batteries make storage much easier.
Ionic liquids are water and metallic salts that can be used to store energy in flow batteries. Nanoflowcell claims that one kilogram of its liquid can store 20 times more energy than what a kilogram worth of lead-acid battery can store, and five times as much as lithium-ion batteries. One kilo gasoline can produce 400 times the energy of lead-acid batteries and 20 times that of ionic liquids from the Swiss company.
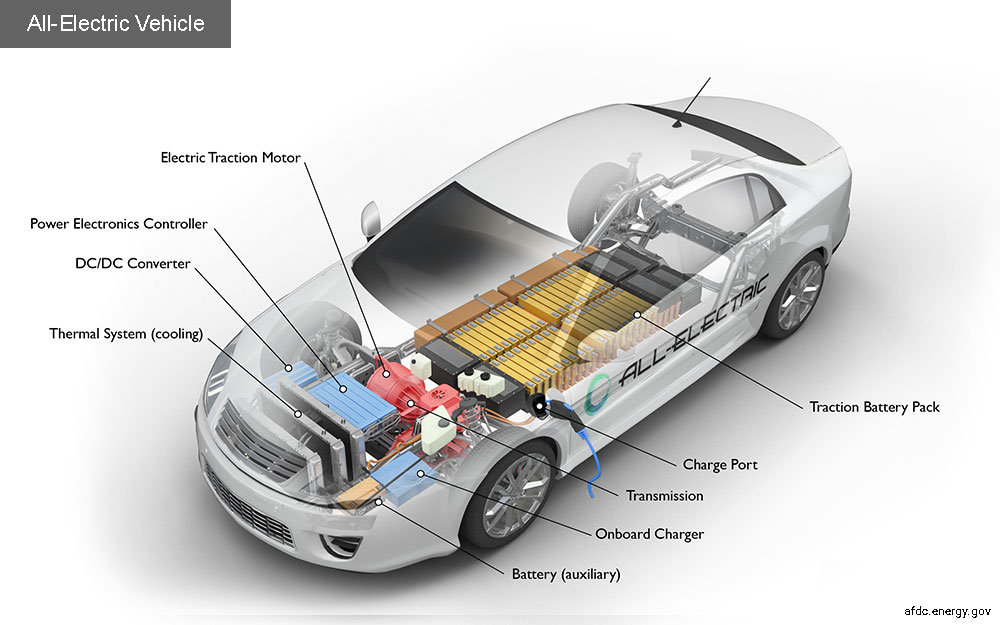
Because they are kept in separate tanks, the liquids do not react to one another. The one for the negatively charged liquid is the other for the positively charged liquid. The membrane allows only the ions to flow between them, which gives the car the energy it needs. After being used to cool the vehicle’s motors and the auxiliary battery, the liquid is then disposed off as vapor. This is illustrated in the diagram below.
Nanoflowcell technology allows liquids to “interact” with a film. This process produces electrical energy. The electrical energy is then delivered to the four motors, one for each wheel and mounted in the middle of the body to avoid excess mass. It is also supplied to the supercapacitors, an auxiliary battery and the supercapacitors, which store the remaining energy.
Quant e-Sportlimousine was the company’s first car. It measured 207.1 inches. (5.26 meters) long, 79.5 in. (2.02 m) wide, 53.5 in. (1.36m) high with a wheelbase 126 in. (3.20 m). Versions were available with 644 (480kW), 912 (680kW) and 1,074 (801kW) horsepower. The maximum range is around 800 km thanks to the 105.7-gallon (480-liter) tanks (50 gallons or 200 liters for each ionic fluid). It was a concept, and it wasn’t sold. This is because there is a technical problem: how would drivers “refuel” their batteries? It will be necessary for the cars to function to have “supply” stations. These stations could look similar to gasoline stations but would require a lot more modifications under the hood.
Nanoflowcell gave the Quantino a height of 153,9 inches. The 3.91 m featherweight Ford Fiesta model is the same size, but the Quant wheelbase is 126 in. (3.20 m). It measures 76 inches. It measures 1.93 m wide by 52,8 inches high. (1.34 m) high. The brand then presented a model that had an electric system of 48V nominal tension (the prior ones were at 735V). The model will be presented in Geneva this year was named after it.
The new car? It is all evidence that this car is an evolution from Quant e-Sportlimousine. See our image comparison below. This is a 48-volt system.
Although the new model appears slightly louder due to the angle of these photos, this could just be printing. A new rear bumper features two vents in place of one on the eSportlimousine’s central one. It can travel 621 miles (1,001 km) at 186 mph (300 kmh). Geneva will have more details. Don’t be surprised by any unexpected results. The flow batteries are truly amazing. These batteries could be the solution to making electric cars more affordable around the globe.